
Handling or transporting heavy machinery is a challenging ride! For instance, moving an excavator from location A to location B involves several considerations: choosing a full-service mover or leasing a truck, assessing temporary storage requirements, planning the ideal machinery arrangement, enabling theft prevention measures, ensuring optimum fuel utilization, complying with regulatory requirements, and more.
Facts indicate that heavy machines play a significant role in the manufacturing sector, accounting for 12% of all production materials needed in the industry. So, if you are a heavy machinery transporter or user, the associated challenges must be considered.
Heavy Machinery Transport & Management and Why Is it Crucial?
Large machinery plays a major role in infrastructure, mining, agriculture, and manufacturing industries. Transporting such machinery requires:
- Expertise in route planning
- A detailed understanding of equipment safety protocols
- Command over an advanced logistics network
Operating heavy machinery poses challenges such as:
- Avoiding fuel theft
- Maintaining optimal running duration
- Performance monitoring, among others
Excavators, bulldozers, construction equipment, and many other types of machinery fall under this category. Several industrial sectors would halt due to inadequate availability or deficient on-site performance.
Issues Faced in Moving Heavy Machinery
Moving heavy equipment involves several challenges:
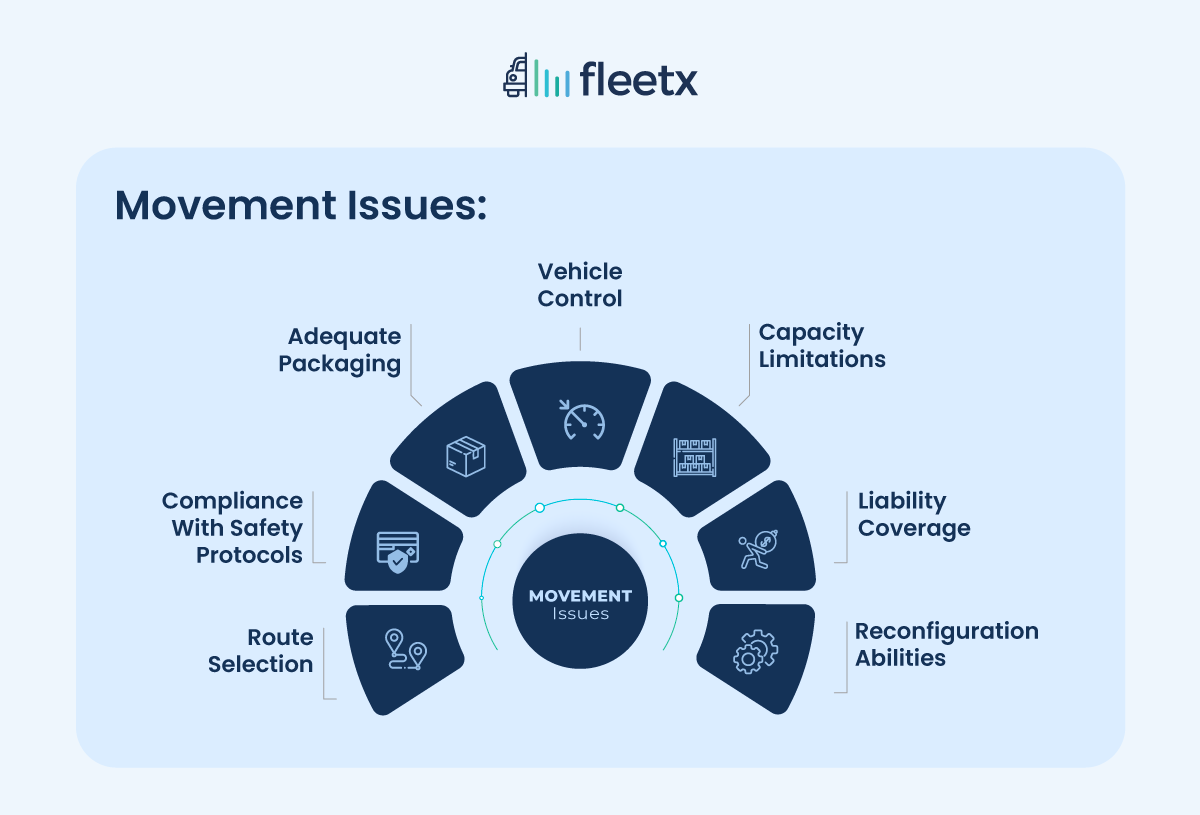
Route Selection: Accurate risk analysis and calculating the most cost-effective route are primary considerations for timely delivery and coordination. Weather conditions and real-time traffic are additional parameters to be considered.
Compliance with Safety Protocols: Shipping heavy machinery on trucks requires adherence to various safety practices. Ensuring machinery safety, adherence to loading and unloading procedures, and securing on-road clearance are vital for a smooth shift.
Adequate Packaging: Accurate packaging material is essential to ensure the safety of the machinery. Vehicles sustain significant shocks while in transit, and the packaging should be sturdy enough to absorb such shocks and prevent damage.
Vehicle Control: Challenges arising from the vehicle used for transportation play a key role in determining the success of the move. Skilled drivers are essential for safely navigating rough terrains, turns, and sudden weather fluctuations.
Capacity Limitations: Oversized equipment must adhere to several size and tonnage regulations. Adequate planning is essential to ensure in-transit safety and fulfilling the regulatory mandates.
Liability Coverage: Despite the best planning, accidents can still occur. Extensive insurance coverage provides security in case of any unfortunate events.
Reconfiguration Abilities: Transporters must possess adequate technical knowledge and attention to detail while dismantling and reassembling heavy equipment. Inaccuracy, of any kind, can lead to significant financial and productivity losses.
Braving transit challenges, when the machinery reaches the site, another set of issues has to be dealt with - the equipment’s day-to-day operations.
Challenges in Heavy Equipment Management

Efficient Fuel Usage: Large machinery consumes massive amounts of fuel. With the ever-rising fuel prices, theft is becoming extremely common at job sites. Pilferage impacts the overall costs incurred by the company or the contractor. The variety of theft mechanisms becomes challenging to deal with.
Asset Downtime and Degradation: Machine breakdowns are sudden but frequent occurrences. Lack of adequate visibility into the machine’s operational schedule and preventive maintenance strategies is a common cause of these issues.
Manual Operation and Reporting Inefficiency: Traditional industry players often overlook the automation benefits in heavy machinery handling. Risks of human errors in heavy equipment usage lead to massive financial losses.
Environmental Impact: A newer challenge is the ecological influence of large machinery usage. Noise and air pollution, toxic discharges, and accidents at sites are significant problems for the contractors.
Consequences of Equipment Supply Chain Disruptions
Ideal conditions dictate a seamless replacement of faulty machinery and the ready availability of required components, at any stage of the production cycle. However, businesses do not operate in ideal ecosystems. Heavy machinery requirement is a difficult task to fulfill, with several logistical issues hampering the process flow. Gaps in the supply chain can lead to-
- Inflated prices of used equipment due to supply delays and shortages from vendors
- Project delays resulting from the unavailability of parts and/or machinery
- High penalties and project costs because of missed deadlines
The Future Outlook
To summarize, stakeholders in the heavy machinery industry face a wide range of challenges. Innovative solutions are key in an industry with such diverse challenges. Proactive adoption of the latest smart practices goes a long way to ensure efficiency, profitability, and long-term growth.






