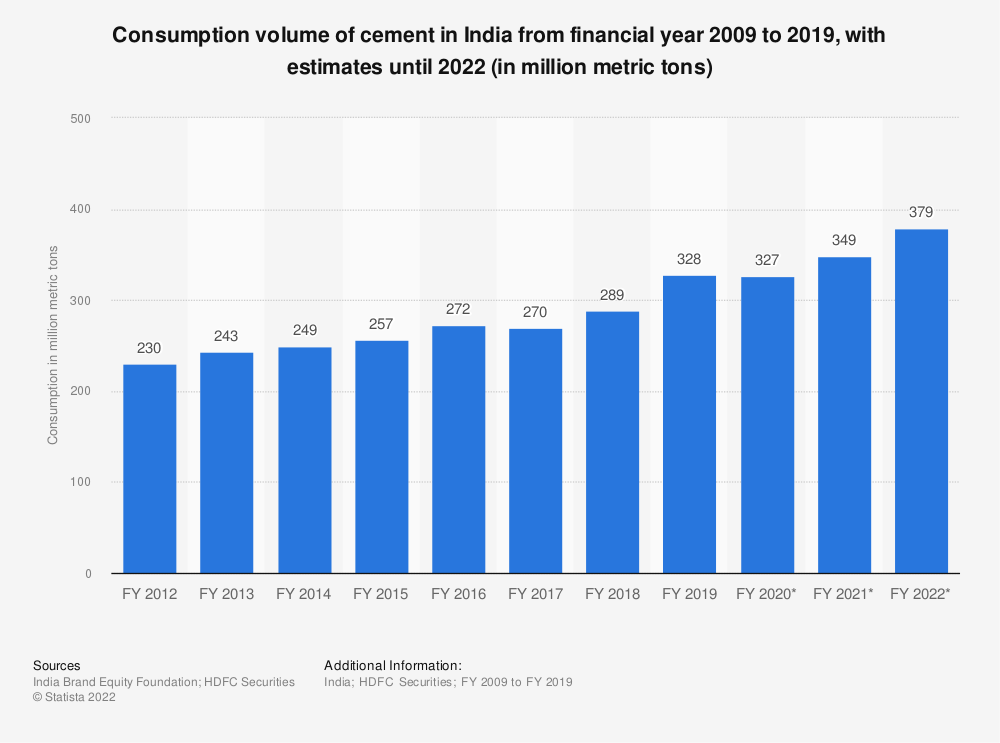
India is the world’s second-largest producer of cement. It accounts for more than 7% of the global installed capacity. Currently, India is producing 278 million tonnes of cement per annum. The industry is expected to reach 550-600 million tonnes per annum by 2025. With the huge growth of the industry, the supply chain of cement in India faces a number of challenges including a lack of visibility and well-developed logistics infrastructure as compared to other developed countries.
The root cause of the problems is that most cement plants are located in remote clusters depending on the availability of limestone. The supply chain in the cement industry is critical to ensure the delivery of cement from these manufacturing locations to the markets. Due to the low value of singular consignments, the logistics cost is much higher compared to other products like fruits, vegetables, consumer appliances, FMCG etc. According to research,
Cement manufacturers invest 50-55% in power & fuel and freight expenses of the total cost and if both inward and outward logistics are combined, it contributes to more than 35 percent of total cement cost.
Hence, optimizing logistics costs has an immediate and visible business impact on cement companies.
With differentiated supply chain systems in rural and urban areas, it becomes very critical to plan and chart out systems for different areas according to the location. The industry faces problems because of poor logistics infrastructure and less investment in technology and automation makes things tougher and more complex. Minimal automation leads to needing for manpower and also can result in inaccuracy.
Common problems faced by the cement industries due to lack of supply chain visibility and the solutions that can be opted:

Unloading point issues
As outbound cement logistics has multiple unloading points, it faces issues in accurate invoice processing. Unloading in different and wrong locations(forward/backward unloading) is one of the major reasons for this inaccuracy. Fleetx AI-based Unloading Point/Points Detection can help in identifying correct unloading points.
Inaccurate billings
The reason for the inefficiencies in billing is because of the contradiction in the actual distance traveled by a vehicle when compared with google distance and distance data stored in the ERP systems.The ERP systems employed by cement companies may synchronize invoice processing with ease with the use of a GPS-based billing system. The GPS-based billing offers a source-to-destination map with the corrected KMs traveling from the source location to the destination location. This is achieved after correcting all the GPS jumps and network issues along the trip. Additionally, it provides information on latest route data(flyovers, new routes, road blockages, etc). This makes GPS billing near accurate.
Speed limit
Big enterprises, like cement companies, are having difficulties in logistics with driver and vehicle safety. These companies have their own safety guidelines, their overall goal of safety is to lower the number of accidents, as well as the repair, downtime, and liability expenses that go along with them but meeting these guidelines becomes really challenging for the companies. Though, a lot of GPS companies provide alerts around harsh Acceleration/braking/cornering, speeding, night driving, continuous driving, etc. But this does not cater to the need of the hour. This need of the hour is to build a database of speed limits state-wise and road-type-wise. Interestingly, one of India’s major cement players is doing the same.
Low investment in Technology
Lack of automation and technology adds to the problem in the cement manufacturing sector. India is manpower surplus, and it is widely believed that labor is a better investment than cutting-edge automation technologies that can possibly eliminate 50% of manual work and human participation. This is the sole reason why investment in India's logistics industry is significantly lower than in other nations. Cement makers have a significant issue because they lack access to innovative and cutting-edge resources that deal with data science, operational automation, and technical trackability. Manual processes allow time, resources, and labor to be wasted. If an issue emerges, a corporation should have a software that can immediately generate a ticket and allocate it to the concerned and the problem may then be fixed right away.
Truck Utilisation
The trucks standing ideal causes great loss to the companies as well as the transporters while a moving truck makes money for both. Trucks should be utilized to the fullest. To reduce the detention time at the plant or the destination, the system should be able to pinpoint the problematic trucks and it should be flagged to the concerned team so that proper action can be taken.
Conclusion
As discussed above, India is a labor surplus and prefers labor over-investing in cutting-edge automation technologies. This becomes a huge reason why the Cement sector faces a lot of problems in the supply chain. Despite the operational and logistical difficulties the cement sector has been growing in India at a handsome pace. New tech-based companies and solutions coupled with government initiatives are assisting cement manufacturers in lowering logistics and freight costs and raising gross profit margins. Undoubtedly manufacturers are under pressure due to the ever rising demand, but it is important to understand that collaborative efforts between cement manufacturers and logistics service providers coupled with technology can make the supply chain process efficient.
What are the main types of cement?
1. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
2. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC)
3. Rapid Hardening Cement
4. Extra Rapid Hardening Cement
5. Low Heat Cement
6. Sulfates Resisting Cement
7. Quick Setting Cement
8. Blast Furnace Slag Cement
9. High Alumina Cement
10. White Cement
How does cement distribution work?
To packing plants, distribution hubs, and marketing districts, deliveries are made through cement plants. The virtual distribution centre serves as a transshipment facility and receives bagged cement deliveries from the cement mill. Bulk cement is being transported from the cement mill to the packaging facility in the meantime.